Tech Tips
Why Wireless Connectivity Is the Next Big Shift in Industrial Automation
Wireless technology and connectivity are reshaping industrial automation. The demand for industrial automation is expected to grow by 9.3% per year to reach $307.7 billion by 2030. And according to the International Federation of Robotics, 4,281,585 robotic units were operating in factories worldwide. That’s an increase of 10%, with annual installations reaching more than half a million units for the third consecutive year.
Automation through Industry 4.0 adoption (the Fourth Industrial Revolution or 4IR), which, according to McKinsey & Company, is ‘the next phase in the digitization of the manufacturing sector, driven by disruptive trends including the rise of data and connectivity, analytics, human-machine interaction, and improvements in robotics.‘
Data and connectivity are everything for industrial automation. Read on to find out why.
What’s Industrial Automation?
First, understanding the concept of industrial automation helps to understand why wireless connectivity is the next big shift.
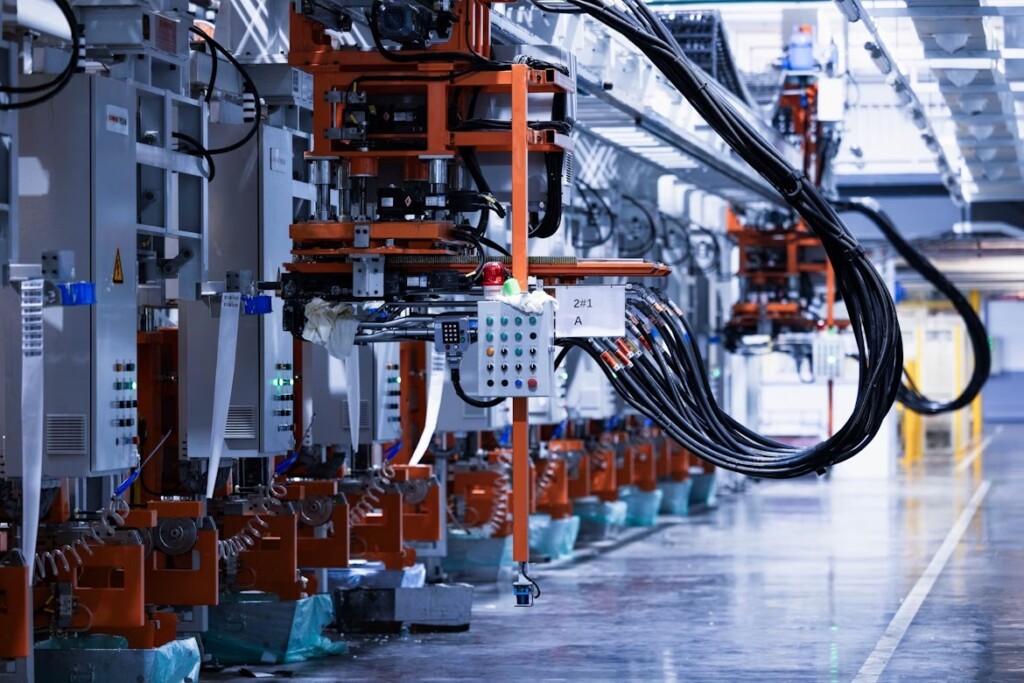
Industrial automation uses technology like advanced computer systems, robots, and control systems to perform and monitor tasks in manufacturing and other industrial processes. The result is a reduced need for human intervention.
Why Wired Connections Are Outdated
Wired connections don’t follow the memo. Traditional wired communications put factory operators behind the competition. They require maintenance, additional setup, and faster rewiring when the old wiring burns out.
Within Industry 4.0 environments, wireless connections such as the technology produced by IO-Link Wireless Technology Leader, CoreTigo, provide significant advantages in installation speed, space optimization, scalability, and adaptability to new AI-driven processes.
Some might say wired systems are more reliable, but that’s a completely outdated statement. Wireless connections are becoming faster, more secure, and more reliable than wired connections ever were.
Wired connections will soon cost more in the long run as wired parts get left behind.
The Future of Wireless Networking
Wireless network and connection adoption was slow. The issue industrial automation faced was the significant cost to upgrade outdated machines to models that ran on wireless connectivity. Statistics show that the average factory still uses legacy equipment and processes.
That said, statistics show 25% of warehouses worldwide had implemented some form of automation by 2024. The change is happening, and the future is wireless networking with technology like the IO-Link Wireless at the forefront of the revolution. And the benefits of IO-Link Wireless seem endless:
- Flexibility for any machine setup
- Faster deployment and changeovers
- Intelligence and data-driven automation
- Lower costs and higher sustainability
Data and control with wireless connections are accessible anywhere, anytime. Many changes and repairs can happen remotely, reducing downtime and additional costs. The prominent demand for greater network capacity, reliability, and deterministic performance is only capable through wireless connectivity.
And since the rapid adoption of the 6 GHz spectrum, a high-frequency band of radio waves (5.925 to 7.125 GHz) that significantly expands the available bandwidth for Wi-Fi, industrial facilities are ready to make wireless LANs the foundation of their automation and digital innovation.
Wireless connectivity isn’t the next big shift for industrial automation; it’s already here. Manufacturers require more capacity, lower latency, and predictable, deterministic networks, and wireless connectivity is the answer.